Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Bruskin, L. G.*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Mase, Atsushi*; Shinohara, Koji; Miura, Yukitoshi
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.6, p.318 - 321, 2004/00
We present a theoretical model of single-frequency microwave reflectometry of plasma density fluctuations with the objective of quantitative estimation of their poloidal spectrum shape and amplitude. The model is based on the analytical solution of the full-wave equation for O-mode microwave propagation inside the plasma in the Born approximation. The solution allows us to find explicitly the poloidal spectrum of weak plasma fluctuations. With the additional assumption of 2D isotropic spectrum in the r- plane it is also possible to find the fluctuation amplitude. We illustrate our model by the analysis of real signals recorded by the O-mode reflectometer on the JT-60U device.
plane it is also possible to find the fluctuation amplitude. We illustrate our model by the analysis of real signals recorded by the O-mode reflectometer on the JT-60U device.
Takei, Nahoko; Nakamura, Yukiharu; Kawano, Yasunori; Tsutsui, Hiroaki*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Tobita, Kenji; Sugihara, Masayoshi; Iio, Shunji*; Shimada, Ryuichi*; Jardin, S. C.*
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.6, p.554 - 557, 2004/00
no abstracts in English
Furukawa, Masaru; Tokuda, Shinji
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.6, p.210 - 213, 2004/00
A model equation for ballooning modes in toroidally rotating tokamaks is derived. It is confirmed that the model equation is appropriate for analyzing the stabilization mechanism of the ballooning modes by comparing the numerical solutions of the model equation with those of the original ballooning equations.
Tokuda, Shinji; Aiba, Nobuyuki*
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.6, p.207 - 209, 2004/00
Recent progress in the theory of the Newcomb equation is reported. Emphasis is put on the analysis of external modes including peeling modes (high  kink modes), where
kink modes), where  is the toroidal mode number. A theory for low
is the toroidal mode number. A theory for low  external modes is developed so that it is also useful for the analysis of resistive wall modes.
external modes is developed so that it is also useful for the analysis of resistive wall modes.
Li, J.; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Miyato, Naoaki; Matsumoto, Taro
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.6, p.585 - 588, 2004/00
An enhanced zonal flow is observed in collisionless electron temperature gradient (ETG) driven turbulence with weak magnetic shears. The Kelvin-Helmholtz (KH) instability is proposed as a primary damping mechanism of such flow. Some considerable evidences for the KH mode excitation are presented. Results seem to suggest a possibility of turbulence transition from the ETG-dominated one to the KH-dominated one due to the zonal flow dynamics in weak shear plasmas.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Tokuda, Shinji; Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.6, p.17 - 72, 2004/00
A global gyrokinetic toroidal particle code for a 3D nonlinear simulation (GT3D) has been developed for a comprehensive study of the ion and electron anomalous transport arising from the ion temperature gradient driven - trapped electron mode (ITG-TEM) turbulence in tokamak plasmas. In the preliminary linear ITG-TEM calculations, basic properties of ITG-TEM modes are confirmed. Adding trapped electrons not only increases the growth rate of the ITG mode, but also produces another unstable electron mode, the TEM mode, which is unstable even at 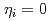 . The dominant mode changes from the ITG mode to the TEM mode depending on
. The dominant mode changes from the ITG mode to the TEM mode depending on 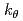 and
and 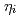 . In linear benchmark calculations using Cyclone base case parameters, eigenfrequencies obtained from GT3D, GTC(PPPL-UCI) and FULL(PPPL) show reasonable quantitative agreement.
. In linear benchmark calculations using Cyclone base case parameters, eigenfrequencies obtained from GT3D, GTC(PPPL-UCI) and FULL(PPPL) show reasonable quantitative agreement.
Matsumoto, Taro; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Li, J.
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.6, p.597 - 600, 2004/00
no abstracts in English
Hoshino, Katsumichi; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Ido, Takeshi*; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Kawashima, Hisato; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Bakhtiari, M.; Shinohara, Koji; Uehara, Kazuya; Oasa, Kazumi; et al.
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.6, p.345 - 348, 2004/00
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Yukiharu; Tsutsui, Hiroaki*; Takei, Nahoko*; Shirai, Hiroshi; Sugihara, Masayoshi; Gribov, Y.*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Tobita, Kenji; Iio, Shunji*; Jardin, S. C.*
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.6, p.196 - 198, 2004/00
no abstracts in English
Miyato, Naoaki; Li, J.*; Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.6, p.581 - 584, 2004/00
Electromagnetic effect on ion temperature gradient driven turbulence and zonal flow generated from the turbulence is investigated based on global electromagnetic Landau fluid simulations in tokamak plasmas. Turbulent transport decreases by increasing beta in a low beta regime. Two types of zonal flow are observed. One is almost stationary flow formed in a low safety factor (q) region, which is weaker at higher beta. The other is flow oscillating coherently at the geodesic acoustic mode (GAM) frequency.